
What Do I Feed My Guinea Pig While She is Pregnant? You need to give your guinea pig freshwater, healthy guinea pig pellets, and hay every day. On their own, guinea pigs don’t produce their own source of vitamin C.
What do you feed a pregnant sow?
Pregnant sows or gilts can be fed sow breeder pellets, milled barley and vegetables. It is important to increase the amount of feed given to the gilt or sow a few days before she farrows. I have a pregnant sow That is due to have little ones this month she just wants to eat corn.
What do pigs eat during pregnancy?
In addition, fish oil, ground shell rock, protein and vitamin concentrates (PROCorm) are added to the diet. In the summer, the diet of pregnant pigs is enriched with various greens. Also at this time of year they can be fed with fresh beans, peas and lupins. They contain a lot of protein, which is necessary for pigs that are expecting offspring.
What is the best feed for pigs?
Feeds should meet the animal’s needs for maintenance, growth, and reproduction, and contain sufficient energy, protein, minerals and vitamins. Farm grains are the most common and best source of food to feed pigs. Most typically corn-based feeds are used because they are high in digestible carbohydrates, low in fiber, and cost effective.
How to increase the appetite of piglets during pregnancy?
A decrease in the norm of food consumed will also beneficially affect the animal’s appetite during the period of feeding piglets. During the second period of pregnancy, a pregnant sow should gain from 25 to 40 kg of weight. For each period of pregnancy in pigs, there is an optimal diet structure. animal feed (5-8%).

How do you take care of a pregnant pig?
Care of the pregnant sow She should be given some feed high in nutrients e.g. grain and greenstuffs every day. Giving the sow access to clean soil or grass with roots from land where no pigs have been kept will allow her to get the minerals she needs. Give the sow plenty of clean bedding when birth is close.
When should I feed my pregnant pig lactating?
Late gestation The energy and nutrient requirements of sows increase with advancing pregnancy especially in the last 10 days of gestation. Therefore, it is recommended that sows be fed 2.0lb extra feed from day 100 of gestation until farrowing.
How many kg of feed does a pregnant pig eat per day?
2-2.5 kgIf the intake is too high during pregnancy and sows become overfat, intake should be reduced while they are lactating. A feeding level of 2-2.5 kg of grain-based feed is suitable for most dry sows. The heavier the sow, the more maintenance that is required and, thus, the greater amount of feed required.
How much protein does a pregnant sow need?
These data suggest that a 260 g/day CP, 12 g/day lysine diet is adequate to support gestating gilt reproduction; however, increased protein levels (260 to 340 g/day CP, 12 to 16 g/day lysine) do increase gilt weight gain during gestation.
How do you increase milk production in pigs?
6 tips for sow milk productionCorrect water intake.Maintain appropriate temperature.Maintain body condition.Support feed intake.Address inflammation (engergy loss)Use Digestarom®
What is the cheapest way to feed pigs?
The last cheap food option for pigs is to feed them compost. Keep a bucket and any food you would normally discard, send it to your pigs. They love table scraps, and it reduces your household waste.
Is salt good for pigs?
The right minerals are essential for muscle, nerve and immune system functions and for sound reproductive health. Salt is especially important for gestating and lactating sows, and can be useful as a carrier for other nutrients essential for swine.
What food makes pigs grow faster?
As an energy source, choose a grain mix of barley, wheat, sorghum and corn for your pig's diet. At least half the mix should be number two yellow corn. Though low in protein, it is considered a primary energy source in pig diets. It is also one of the most economical feedstuffs available for swine production.
Do you mix pig feed with water?
According to Brooks [1], mixing water with dry feed and feeding after a few minutes ensures that pigs receive a more homogeneous diet and increases the rate of hydration, especially if it is finely ground, favoring the action of both digestive and in-feed enzymes.
How much should I feed a pregnant pig?
Sow Gestation Rations Adequately conditioned sows can be fed roughly 4-to-6 pounds of feed per sow per day during gestation, while under-conditioned sows, first parity sows and gilts require additional nutrients through the entire gestation period for maternal weight gain.
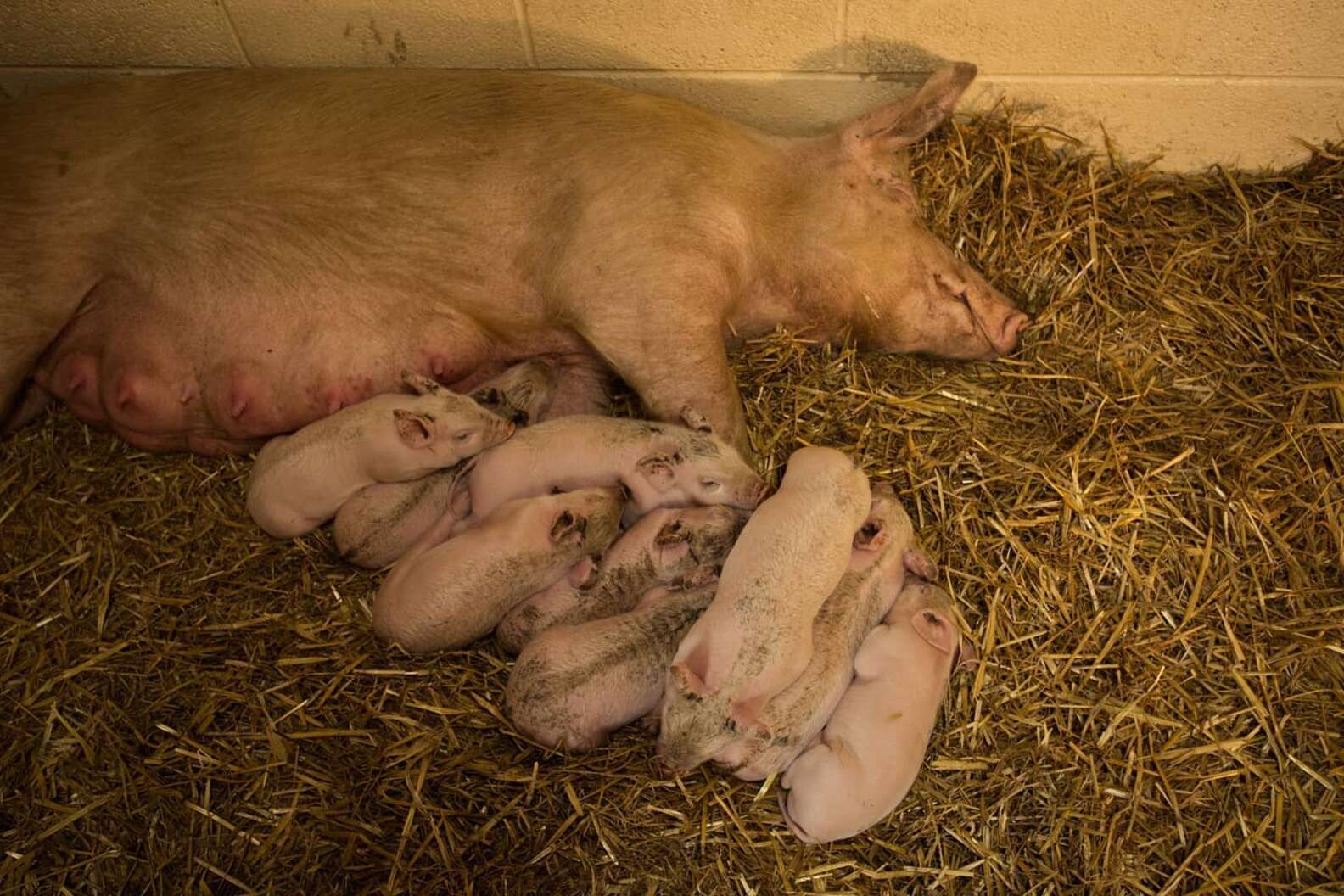
What should a pig eat after giving birth?
colostrumAll newborn pigs should receive colostrum. Extra care for weak or small pigs and for large litters can result in more pigs weaned. In the first few days after farrowing, observe sows and pigs carefully for evidence of disease condition or inadequate milk production or intake.
Why is my pregnant pig not eating?
The 'common-sense' standard operating practice is not to feed during parturition. It is most likely that the sow will not eat at this time. They will also be less likely to eat during early labour, prior to the birth of the first pig. In the two to 24 hours before farrowing, most females are fed.
How much should I feed my lactating pig?
A feed allowance of 4.0lb (approximately 1.0% of the sows weight for the sow) plus 1.25lb for each pig in the litter is a good guide to the minimum levels lactating sows should be fed. Formulation of herd specific diets can be accomplished by estimating sow feed intake and litter weight gain.
What is the best feed for lactating sows?
Lactating sow feeds should be formulated with a low crude protein, low fermentable carbohydrate (FCHO) and a high amount of glucogenic nutrients (starch + sugars) in order to stimulate feed intake, increase milk production and reducing weight loss.
How much feed does a lactating sow need?
Sows at the Purina Animal Nutrition Center are fed an ad libitum ration through the entire lactation period, with fresh feed supplied each day. On average, each sow consumes between 14 and 15 pounds of feed per day during the period.
How do you take care of a lactating sow?
Decreasing the effective environmental temperature, increasing the nutrient density of the lactation diet, maintaining fresh adequate supplies of feed and water, and preventing excess weight gain during the prior gestation period will increase nutrient intake during lactation.
What is the purpose of breeding pigs?
The purpose of the breeding herd is to consistently produce a targeted number of high quality weaned pigs in an efficient manner and at low cost. Feed costs in the breeding herd constitute about 12% of the cost of producing a market hog. More importantly, the feeding program in the breeding herd can significantly influence sow productivity and longevity in the herd. Most costs, including feeding costs, in the breeding herd are fixed costs and therefore, increased breeding herd efficiency will reduce overall production costs. Therefore, there is considerable scope to reduce input costs and increase production efficiency through improvement in the feeding of the gestating and lactating sow.
How to optimize sow reproductive performance?
An essential part of any strategy to optimize sow reproductive performance, increase efficiency of feed usage and lower culling rate, is to control weight and backfat gain during gestation and weight and backfat loss in lactation. This is best achieved by individually feeding each sow a well balanced diet, and basing daily feed allowances according to an estimate of sow bodyweight and backfat thickness.
What should a feeding program be based on?
The feeding program should be based on some estimate of sow weight, backfat and/or body condition at the time of breeding. This program should be designed to:
What is the purpose of feeding gestating sows?
The objective of the feeding program for gestating sows is to achieve an appropriate, targeted sow weight gain during gestation that will allow optimum litter development and prepare the sow for lactation.
How to determine feeding allowances for a sow?
A spreadsheet can be developed to determine the daily feeding levels for each sow based on her weight and backfat level at breeding. These feeding allowances also take into account the sow weight gain needed to attain the targeted increase in backfat required for each sow. The maintenance requirement is then calculated on the predicted midgestation sow weight. Therefore, these feeding levels can be fed from breeding to day 100 of gestation.
How much energy does a sow need to produce a litter?
But these tissues are very high in water content and therefore only require about 3-5% of the sow’s energy requirement, usually 0.2–0.3 Mcal ME per day. Because the developing litter has a very high priority for nutrients, feeding levels during gestation have to be very low before they will reduce litters size or birth weight of sows that are in normal body condition.
How does feeding affect a herd?
More importantly, the feeding program in the breeding herd can significantly influence sow productivity and longevity in the herd. Most costs, including feeding costs, in the breeding herd are fixed costs and therefore, increased breeding herd efficiency will reduce overall production costs. Therefore, there is considerable scope ...
How does nutrient intake affect pigs?
Extreme reductions (50 to 60%) in nutrient intake of pregnant sows will reduce birth weight of pigs and decrease muscle fiber numbers at birth. These low birth weight pigs can have decreased growth performance to market, decreased lean content of carcasses at harvest and compromised meat quality compared to pigs with normal birth weight [10]. If severe restrictions in nutrient intake will compromise performance of the offspring, will elevated nutrient intake of pregnant sows during specific periods of gestation improve performance of pigs? In general, increased nutrient intake of sows does not seem to improve performance of offspring to slaughter weight. The elevated plane of nutrition for pregnant sows may benefit low weight fetuses present in the uterus but this theory has not been proven.
What is feeding during gestation?
Feeding management during gestation focuses on minimizing embryo and fetal losses and on preparing the sow for farrowing and lactation. In the very early stages of gestation immediately after conception, the first objective is to provide conditions that will ensure maximal survival of embryos and favor a large litter size at the subsequent farrowing. Growth of the developing fetuses in conjunction with increasing nutrient stores in the sows body through continued growth of young sows or replenishment of nutrient stores lost during the previous lactation for older sows are the main objectives during mid-gestation (day 30 to 75). In late gestation, fetal growth continues at a very rapid rate and mammary development occurs in preparation for the upcoming lactation. Proper feeding programs will satisfy these nutritional needs and ensure continued reproductive performance of sows at a reasonable cost.
How does fiber help a swine?
Dietary fiber. The gestating sow seems to be the most capable class of swine in modern production systems to effectively utilize dietary fiber. The need to limit energy intake for the control of gestation weight gain makes the gestating sow a logic choice to consume fibrous feedstuffs as part of the diet. Fiber can serve as a laxative agent and may improve comfort of sows fed limited quantities of feed. Dietary fiber decreases the energy and bulk density of the diet which limits energy intake and thus controls body weight gain without severely restricting total feed intake. Allowing sows to consume a larger quantity of feed decreases expression of stereotypic behaviors, increases level of satiety in the sow, and presumably improves well being of the sow. Feeding relatively large quantities of a bulky diet throughout gestation can enhance voluntary feed intake of sows during the subsequent lactation [16]. Dietary fiber offered during gestation can increase litter size at the subsequent farrowing but the response can be variable [17]. Litter size weaned may be improved about 0.5 pigs/litter when fiber is added to the sow diet during gestation. Some nutritionists [18] have suggested sows consume 350 to 400 g/d of neutral detergent fiber (NDF) to maximize the chance of an improvement in sow reproductive performance. Diets containing 45% wheat midds, 20% soybean hulls, 25% alfalfa meal, 30% sugar beet pulp, or 40% oats provide sows about 350 g/d of NDF when fed at 6 Mcal ME daily. However, others have reported no improvement in litter size farrowed or weaned when sows consumed high fiber diets during gestation [17, 19]. Fiber characteristics differ among fibrous feedstuffs. It appears that most of the beneficial effects of dietary fiber are realized when ingredients high in soluble fiber, such as sugar beet pulp, are included in the diet.
How to weigh sows?
The best way to do this is to weigh sows with a livestock scale. The only true replacement for a livestock scale is another livestock scale! Visual assessments of body weight are not accurate. On many farms, installing a scale in a common hallway between gestation quarters and farrowing rooms allows workers to weigh sows as they enter the farrowing room and when they leave at weaning. All the sows do not have to be weighed to paint a useful picture of sow weight changes in the operation. Weighing ten to twenty sows from each parity group (Parity 0, 1, 2, 3-5, and 6+) and each season (summer, spring/fall, and winter) will suffice if labor and time constraints prevent weighing all sows. This information is extremely important to allow evaluation of both the gestation and lactation feeding programs and to aid in fine-tuning the feeding program.
Why do sows need maintenance feed?
With this approach, sows are fed maintenance levels of feed in the early portion of gestation (day 0 to 30) because nutrient needs of the developing litter are extremely small. In addition, high level feeding in this very early phase can have detrimental effects on embryo survival before implantation [1].
Why do sows become catabolic during pregnancy?
Modern productive sows will likely become catabolic (use body stores of nutrients) during the late phases of gestation because nutrient supply from feed intake will not satisfy daily nutrient needs.
How are nutrient requirements influenced by the sow?
Nutrient requirements for maintenance are influenced primarily by body weight of the sow and the environment in which the female is housed. Older, heavier sows have increased nutrient needs and will require more feed to maintain their body than younger, lighter sows.
What is the best day to feed a baby pig?
The level of nutrition from day 21 to 50 may also be important to maximize the number of muscle fibers in piglets born. Primary muscle fibers set the stage for how fast and lean the baby pig can grow after birth and may therefore affect subsequent nursery and growing-finishing pig performance.
How much feed is needed for a sow?
To meet the energy requirement of a sow at mating, 3.9 lbs. of feed is needed, whereas 5.3 lbs. is required for a sow at the end of gestation. If we do the calculation based on lysine, the average lysine requirement during gestation can be met with 3.6 to 4.0 lbs. of feed.
What is the proper nutritional management of gestating sows?
Proper nutritional management of gestating sows includes feeding the correct nutrient levels to meet the sow's requirement, but also correct management of feed amounts given to the sows at critical times in their development.
When do piglets develop muscle fibers?
These muscle fibers develop between day 21 and 50 of gestation and their number can be affected by nutrition. In studies where feed intake of sows was severely restricted during gestation, growth of piglets after birth was reduced (Pond et al. 1985, Pond and Mersmann, 1988).
Can you feed a sow ad libitum?
Allowing sows to consume feed ad libitum between weaning and breeding may be a prudent practice, however, to help sows recover from weight loss during lactation and take advantage of a possible increase in ovulation rate and shorter weaning to breeding interval. Early Gestation.
What is the main food of a pig?
Water is the central part of a pig’s diet. One-half to two-thirds of its body weight is water . Access to clean drinking water is essential to a pig’s growth rate. Newly weaned pigs are especially prone to dehydrate. However water is supplied, water devices must be sanitized and properly positioned.
Why are pigs important?
Pig temperature requirements are important to growth and production . Pigs are a highly adaptable animal and can perform well within a range of temperatures. However, temperatures too low or too high can have adverse effects on stock.
What is the most important part of swine production?
The most important part of swine production is in knowing the correct way to feed pigs. Whether browsing through a piglet feeding guide or studying swine management techniques, pigs need a high energy diet that is low in fiber that contains ample protein. Pigs will consume enormous amounts of food quickly.
How much weight do pigs gain?
With a proper diet, expect weight gains of about 1.5 to 1.7 pounds per day up to approximately 110 pounds.
Why is it important to keep pigs cool in summer?
If, for example, temperatures are too cold, a pig will feed more but expend more energy to stay warm, resulting in slow growth. Hot weather can lead to heat stress and reduce feed consumption (and can possibly lead to death), so it is important to keep livestock cool in summer. Consequently, growth and mature rates slow, conception rates fall, and pig flow is reduced, disrupting stock levels. Depending on the season, keep buildings well-ventilated or heated, and provide adequate air space within the pen to ensure pig growth and production rates are maintained.
How much should a piglet weigh?
Piglets, younger pigs that weigh less than 40 pounds, should be introduced to a solid diet through creep feeding while they are still suckling. Dietary needs will increase daily with a pig’s weight.
What foods slow down growth?
Fish. Meat. Fruits. Potatoes. Foods high in sugars can slow growth rates while milk, meats, and fish can harbor viruses. Pits and seeds of apples, pears, apricots and peaches contain a naturally occurring substance called amygdalin which is a cyanogenic glycoside that is released when chewed causing illness, discomfort, or even death.
Introduction
Objectives
Feeding For Lifetime Productivity
Guides to Determining Feeding Allowances
Estimating Sow Feed Allowance
Backfat Measurement
Measuring Backfat
Suggested Feeding Allowances For Gestating Sows
Pattern of Feeding
Late Gestation
- The energy and nutrient requirements of sows increase with advancing pregnancy especially in the last 10 days of gestation. Therefore, it is recommended that sows be fed 2.0lb extra feed from day 100 of gestation until farrowing. This higher level of feeding will prevent loss of sow condition (body stores) and prepare sows for increased feeding lev...