
They feed on bacteria, protozoa, fungal spores, and other decaying organic material. The plasmodium of Physarum polycephalum is a bright yellow glistening multinucleate mass that can move in an amoeboid fashion. It ingests solid food particles in the same manner as an amoeba and can also absorb dissolved nutrients.
What do Physarum polycephalum eat?
They feed on bacteria, protozoa, fungal spores, and other decaying organic material. The plasmodium of Physarum polycephalum is a bright yellow glistening multinucleate mass that can move in an amoeboid fashion. It ingests solid food particles in the same manner as an amoeba and can also absorb dissolved nutrients.
How does polycephalum polycephalum respond to multiple food sources?
When grown in a maze with oatmeal at two spots, P. polycephalum retracts from everywhere in the maze, except the shortest route connecting the two food sources. When presented with more than two food sources, P. polycephalum apparently solves a more complicated transportation problem.
How do you grow slime mould Physarum polycephalum?
Top Tips for growing Physarum Polycephalum... If you're keen to grow your own the slime mould Physarum Polycephalum, this information may help... Preferred conditions: dark and damp (for example: petri dishes or tupperware in a shoe box or similar, with a damp base - paper towels or agar base).
What is the function of the plasmodium in Physarum polycephalum?
The plasmodium of Physarum polycephalum is a bright yellow glistening multinucleate mass that can move in an amoeboid fashion. It ingests solid food particles in the same manner as an amoeba and can also absorb dissolved nutrients. It crawls towards its food, surrounds it, and secretes enzymes to digest the food.
What is a slime molds favorite food?
In one study, researchers set out dabs of oatmeal (a favorite food for slime molds in the laboratory, Dussutour said) mimicking the location of cities around Japan. Slime mold let loose on this playground of food formed a network that beautifully mimicked Japan's rail system.
How do you grow Physarum?
Top Tips for growing Physarum Polycephalum...Preferred conditions: dark and damp (for example: petri dishes or tupperware in a shoe box or similar, with a damp base - paper towels or agar base).Food likes: favourite food is porridge oats, doesn't mind starchy stuff like rice and pasta.More items...•
What do cellular slime molds feed on?
Cellular slime molds are eukaryotic microorganisms in the soil. They feed on bacteria as solitary amoebae but conditionally construct multicellular forms in which cell differentiation takes place.
What does slime mold need to grow?
Slime mold is made up of organisms that resemble amoebas (single-celled organisms with no definite shape) and can easily be described as “blobs.” They move around looking for food and avoiding predators. They need food and water to live, and like cool, dark places.
What kills Physarum polycephalum?
Re: Physarum polycephalum To kill the fungus, you can use apple cider vinegar (add 1 tablespoon of it in about 1 cup of water) or milk (just a little bit) to kill the fungus.
How fast does Physarum polycephalum move?
The plasmodium of myxomycetes, and especially that of Physarum polycephalum is known for its cytoplasmic streaming. The cytoplasm undergoes a shuttle flow rhythmically flowing back and forth, changing direction typically every 100 seconds. Flows can reach speeds of up to 1mm/s.
What kills slime molds?
If you want this interesting-looking visitor gone, any of the organic fungicides will kill it. Slime mold, as well as any mushrooms or toadstools, can be knocked out with baking soda, potassium bicarbonate, cornmeal, cornmeal tea, hydrogen peroxide, or commercial products like BioSafe Disease Control.
How do slime molds get their energy?
These organisms exhibit properties of both fungi and protists. The slime molds and the water molds are members of this group. They all obtain energy by decomposing organic materials, and as a result, are important for recycling nutrients. They can be brightly colored and live in cool, moist, dark habitats.
Can slime mold infect humans?
Slime molds are not known to be a danger to human or animals. Chemical treatment is not warranted for this problem. These organisms are very sensitive to the environment.
How do slime molds eat?
Slime molds go through a process called "phagocytosis" in order to gain the necessary nutrients. This simply means that the slime mold engulfs its food items and internally digests it.
Can you keep slime mold as a pet?
Keeping slime moulds as 'pets' The slime mould Physarum polycephalum is very easy to keep, it's harmless and undemanding, it can live on a sheet of kitchen towel in an old margarine tub and needs just oats for food. Making maps and mazes for them to solve and explore is easy to do.
How fast do slime molds grow?
Within 24–48 hours, the plasmodial slime mold will begin to spread across the surface of the filter paper and engulf the oat- meal.
Can you grow slime mold at home?
Introduction: How to Grow SLIME MOLD These organisms are often miscatagorized as fungi or bacterium but they are actually a single cell organism with multiple nuclei known as a protist and they are also extremely easy to cultivate at home!
How long does slime mold take to grow?
Within 24–48 hours, the plasmodial slime mold will begin to spread across the surface of the filter paper and engulf the oat- meal.
Can you keep a slime mold as a pet?
Keeping slime moulds as 'pets' The slime mould Physarum polycephalum is very easy to keep, it's harmless and undemanding, it can live on a sheet of kitchen towel in an old margarine tub and needs just oats for food. Making maps and mazes for them to solve and explore is easy to do.
Where can I find Physarum?
In nature, Physarum polycephalum is found in multiple environments; however, the organism is most commonly found in cool, humid, dark places such as leaf litter and other organic debris in forests.
What is P. polycephalum used for?
P. polycephalum is used as a model organism for research into motility, cellular differentiation, chemotaxis, cellular compatibility, and the cell cycle .
When nutrients are provided uniformly, the nuclei in the plasmodium divide synchronously?
When nutrients are provided uniformly, the nuclei in the plasmodium divide synchronously, accounting for the interest in using P. polycephalum as a model organism to study the cell cycle, or more specifically the nuclear division cycle. When the plasmodium is starved, it has two alternative developmental pathways.
What is the name of the plant that grows from an oat flake?
Physarum polycephalum growing from an oat flake (center) towards hairy roots of the plant Valeriana officinalis (left). Physarum polycephalum has been shown to exhibit characteristics similar to those seen in single-celled creatures and eusocial insects.
What happens when plasmodium is starved?
When the plasmodium is starved, it has two alternative developmental pathways. In the dark, the plasmodium typically differentiates reversibly into a dormant “sclerotium” (the same term is used for dormant forms of fungal mycelia, but the myxomycete sclerotium is a very different structure).
Where does apogamic development occur?
Apogamic development can also occur in nature in various species of myxomycetes. In the figure of the P. polycephalum life cycle, the typical haploid-diploid sexual cycle is depicted in the outer circuit and the apogamic cycle in the inner circuit.
Can a polycephalum plasmodia be haploid?
In laboratory strains carrying a mutation at the matA mating type locus, the differenti ation of P. polycephalum plasmodia can occur without the fusion of amoebae, resulting in haploid plasmodia that are morphologically indistinguishable from the more typical diploid form.
Can plasmodium grow in a foot?
While nutrients are available, the network-shaped plasmodium can grow to a foot or more in diameter. Like amoebae, the plasmodium can consume whole microbes, but also readily grows axenically in liquid cultures, nutrient agar plates and on nutrient-moistened surfaces.
How to grow slime mold?
Place a few flakes of rolled oats directly on top of the slime mold culture. Next, place a few flakes of rolled oats on the other side of your barriers. Slime mold does not like light so store your slime mold plates in a warm dark place. Now let your slime mold grow and watch it in action! Ask Question.
How to grow microbes in a small pot?
Agar is a seaweed based gelatin that is used as the medium to grow microbes. Start by mixing 1 tablespoon of agar with one cup of COLD water in a small pot. (If the agar is mixed into the water after it is heated, the agar will clump together unevenly.)
Why did the plates with the triple antibiotic have little to no fungus growth?
Additionally, he speculated on why the plates with the triple antibiotic had little to no fungus growth: "It probably has to do with the nutritional requirements of the fungus. It is also possible that the antibiotics inhibit the fungal growth.". There you have it!
Can you squeeze triple antibiotics on agar plates?
The triple antibiotic was easy to squeeze on the agar. The salt and the cayenne pepper were made into a paste in order to apply them evenly onto the agar plates. Ask Question.
Overview
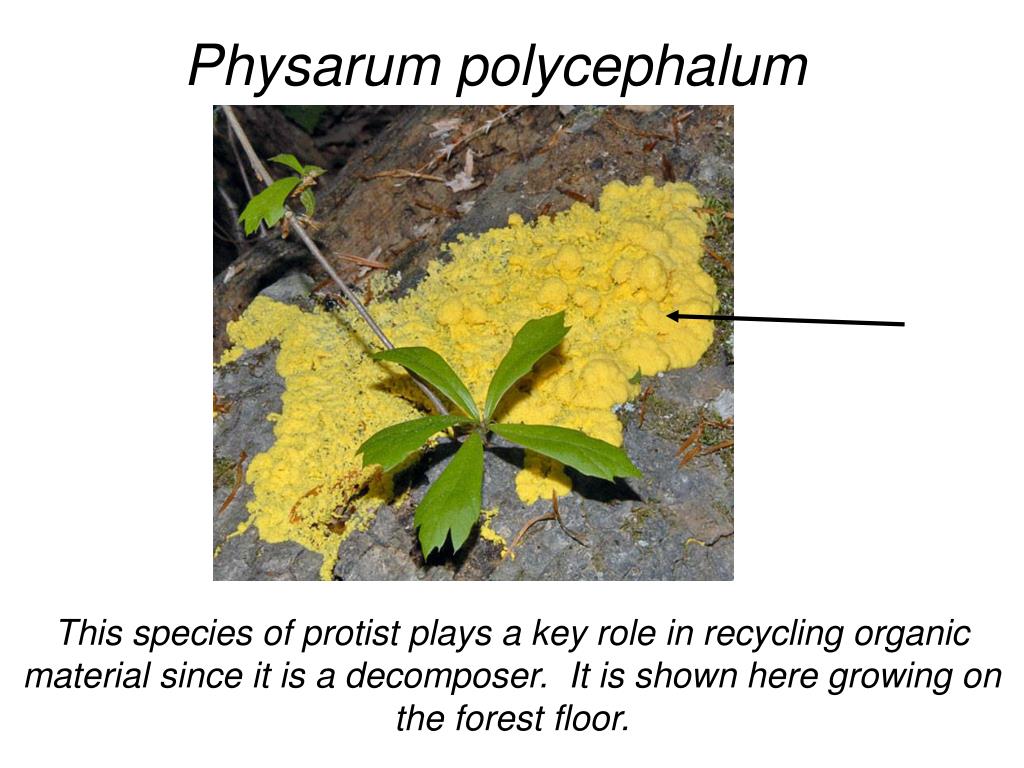
This observational microbiology activity introduces students to a slime mold from the genus Physarum, a decomposer found in cool, humid, dark places like the forest floor.
Activity Objectives
Observe the phenomenon of periodic streaming in Physarum polycephalum.
Safety & Disposal
Use this activity only in accordance with established laboratory safety practices, including appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, chemical splash goggles, and lab coats or aprons. Ensure that students understand and adhere to these practices.
Procedures
A Physarum plate culture comes ready to use or subculture for additional group samples. When the culture arrives, immediately open the shipping container and remove and inspect the culture. The plasmodium is a yellow growth on the surface of the agar. Ensure that the plates are not cracked and the lids are securely taped.
Data and Observations
Student answers will vary but should include observations of streaming and the plasmodium moving toward the food supply, possibly on several fronts. Over 24 hours, the plasmodium should increase in area, and mass will probably remain unchanged.

Overview
Situational behavior
Physarum polycephalum has been shown to exhibit characteristics similar to those seen in single-celled creatures and eusocial insects. For example, a team of Japanese and Hungarian researchers have shown P. polycephalum can solve the shortest path problem. When grown in a maze with oatmeal at two spots, P. polycephalum retracts from everywhere in the maze, except the shortest rout…
Life cycle and characteristics
The two vegetative cell types, amoebae and plasmodia, differ markedly in morphology, physiology and behavior. Amoebae are microorganisms, typically haploid, that live primarily in the soil, where they phagocytose bacteria. In the laboratory, amoebae are grown on lawns of live or dead Escherichia coli on nutrient agar plates, where they can multiply indefinitely. Axenic culture of amoe…
Cytoplasmic streaming
The plasmodium of myxomycetes, and especially that of Physarum polycephalum is known for its cytoplasmic streaming. The cytoplasm undergoes a shuttle flow rhythmically flowing back and forth, changing direction typically every 100 seconds. Flows can reach speeds of up to 1mm/s. Within the tubular network flows arise due to the cross-sectional contractions of the tubes that are generated by the contraction and relaxation of the membranous outer layer of the tubes enri…
Innate immunity
P. polycephalum produces its own anti-viral substances. Mayhew & Ford 1971 find an extract of P. polycephalum prevents some crop diseases: Tobacco mosaic virus and tobacco ringspot virus are inhibited by a product of P. polycephalum. Both Nicotiana tabacum and the beans Phaseolus vulgaris and Vigna sinensis suffered almost no lesioning in vitro from TMV or TRSV when treated with a P. polycephalum extract. However, the southern bean mosaic virus was unaffected.
Sources
• Gawlitta, W.; Wolf, K.V.; Hoffmann, H.U.; Stockem, W. (1980). "Studies on microplasmodia of Physarum polycephalum". Cell and Tissue Research. 209 (1): 71–86. doi:10.1007/bf00219924. PMID 7191783. S2CID 23561113.
• Henry Stempen; Steven L. Stevenson (1994). Myxomycetes. A Handbook of Slime Molds. Timber Press. ISBN 978-0-88192-439-8.
External links
• Dussutour, Audrey. Talk given by a French slime mold specialist (video). TEDx. Archived from the original on 2021-12-19 – via youtube. (in French, with English subtitles available)
• "PhysarumPlus". An internet resource for students of Physarum polycephalum and other a-cellular slime molds
• Ball, Philip (2008). "Cellular memory hints at the origins of intelligence". Nature. 451 (7177): 385. Bibcode:2008Natur.451..385B. doi:10.1…
• Dussutour, Audrey. Talk given by a French slime mold specialist (video). TEDx. Archived from the original on 2021-12-19 – via youtube. (in French, with English subtitles available)
• "PhysarumPlus". An internet resource for students of Physarum polycephalum and other a-cellular slime molds
• Ball, Philip (2008). "Cellular memory hints at the origins of intelligence". Nature. 451 (7177): 385. Bibcode:2008Natur.451..385B. doi:10.1038/451385a. PMID 18216817. S2CID 4423452. The learni…