If your child has galactosemia, it’s important that they avoid foods and drinks that contains milk, and any other food or drink that has galactose in it, for the rest of their lives. Instead of milk, babies can be given special formula, such as: Formula that uses soy
What foods should be avoided in galactosaemia?
To follow a low-galactose diet, avoid foods with lactose, including:
- milk
- butter
- cheese
- ice cream
- other dairy products
Do children grow out of galactosemia?
Children do not grow out of classic galactosemia. It is an inherited disease that they will have for the rest of their lives. An infant or child with classic galactosemia cannot break down the simple sugar galactose. Therefore, they must avoid consuming milk, dairy products, and other foods that contain galactose.
How do I choose the best baby formula for galactosemia?
- The texture of this formula is a little heavy, but it tastes delicious.
- It is formulated with a special mix of minerals and nutrients to help resolve the symptoms of colic in babies.
- Help lower abdominal and wind discomfort in babies.
- Car for your baby with important daily minerals and nutrients.
Is there a cure for galactosemia?
The most common treatment for galactosemia is a low-galactose diet. This means that milk and other foods that contain lactose or galactose can’t be consumed. There is no cure for galactosemia or approved medication to replace the enzymes.

What do you feed a child with galactosemia?
A child on a galactose-restricted diet can eat most foods containing protein, such as beef, poultry and eggs. They can also eat most types of fruits, vegetables, and grains. Since children with galactosemia cannot consume milk products, their calcium levels may be too low.
What can you eat with galactosemia?
These are allowed as they do not contain lactose or galactose.Meat, poultry and fish. Fresh meat, chicken or turkey.Eggs. Eggs cooked with milk substitute and milk-free margarine.Fruit and nuts. All fresh, frozen and dried fruit.Flours, grains and pasta. ... Bread, biscuits and cakes.
Is breastmilk good for galactosemia?
In terms of infant conditions, galactosemia is clearly an absolute contraindication to breast-feeding. Breast milk is a rich source of lactose, and the very survival of infants with galactosemia is dependent on their receiving a non-lactose-containing formula.
What can you not eat when you have galactosemia?
Food Ingredients which are unacceptable in the diet for Galactosemia:Butter.Buttermilk.Buttermilk Solids.Cheese (EXCEPTIONS: Jarlsberg, Gruyere, Emmentaler, Swiss, Tilster, grated 100% Parmesan, Parmesan aged >10 months, and sharp Cheddar cheese aged >12 months)Cream.Dry Milk.Dry Milk Protein.Dry Milk Solids.More items...
What foods are high in galactose?
Galactose Rich FoodsFormulated bar, SLIM-FAST OPTIMA meal bar, milk chocolate peanut (5.62g)Honey (3.1g)Dulce de Leche (1.03g)Celery, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt (0.85g)Celery, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt (0.85g)Beets, canned, regular pack, solids and liquids (0.8g)More items...
What formula is good for galactosemia?
The powdered form of soy formula is generally preferred for babies with Galactosemia. This formula is also very low in galactose; however, most formulas have "carrageenan" in them.
Is lactose free milk suitable for galactosemia?
Although it is lactose free, the galactose levels are still very high in the product. Therefore these products are NOT suitable for people with Galactosaemia. These products now include milk, cheese, yoghurts, cream and spreads.
What happens if someone with galactosemia eats dairy?
Babies and children with galactosemia need to avoid eating or drinking anything that has milk in it, whether from breastfeeding or from an animal. If they get too much galactose, it may damage their liver, kidneys, eyes, or brain.
Can babies outgrow galactosemia?
Galactosemia is a lifelong condition that children will not outgrow. However, galactosemia can be easily managed by following a galactose-free diet. Galactose is derived from the complex sugar, lactose, so any food containing lactose (milk and milk products) should be avoided as well.
What fruits and vegetables contain galactose?
Galactose contents ranged from less than 0.1 mg per 100 g of tissue in artichoke, mushroom, olive, and peanut to 35.4 mg per 100 g in persimmon. Fruits and vegetables with over 10 mg per 100 g included date, papaya, bell pepper, tomato and watermelon.
Do bananas contain galactose?
) reported a wide range of soluble galactose contents in a survey of 45 fruits and vegetables. For example, apples, bananas, pears, carrots, peas, and sweet potatoes each contained 5 to 10 mg galactose per 100 g final weight, whereas apricots provided less than 2 mg galactose per 100 g final weight.
What foods are lactose free?
Food and drinks that do not usually contain lactose include:soya yoghurts and cheeses.coconut-based yoghurts and cheeses.almond milk, yoghurts and cheeses.rice milk.oat milk.hazelnut milk.foods with the "dairy-free" or "suitable for vegans" signs.carob bars.
What foods are lactose free?
Food and drinks that do not usually contain lactose include:soya yoghurts and cheeses.coconut-based yoghurts and cheeses.almond milk, yoghurts and cheeses.rice milk.oat milk.hazelnut milk.foods with the "dairy-free" or "suitable for vegans" signs.carob bars.
What is the life expectancy of someone with galactosemia?
With a galactose-restricted diet patients have a normal life expectancy. However, patients may still suffer long-term complications such as problems of mental development, disorders of speech, hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism and decreased bone mineral density (Bosch 2006).
Can galactosemia go away?
There is no cure for classic galactosemia; instead, children are treated with a special galactose-free diet in which they avoid all milk and milk-containing products as much as possible for the rest of their lives.
What happens if galactosemia is not treated?
A. Untreated galactosemia can cause rapid, unexpected death due to an infection that invades the blood. Infants with untreated galactosemia may also develop brain damage, liver disease, and cataracts. Each child with galactosemia is different so the outcome will not be the same for all children.
What is the shock of having a baby diagnosed with Galactosemia?
The shock of diagnosis and what's next. Having your baby diagnosed with Classic Galactosemia can be upsetting and disorienting for you as a family. You may be feeling anxious as symptoms develop. And, you're probably thinking a lot about how you'll rise to the challenge of keeping your baby healthy.
What is the test for galactose?
Some states may also perform an additional test to measure Total Galactose (galactose + Gal-1p). When a doctor believes a newborn may have Galactosemia, the parents will be instructed to immediately switch their baby from milk to a soy or elemental formula, and to stop breastfeeding until the diagnosis can be confirmed.
Why is soy formula low in galactose?
This formula is very low in galactose because it is made from a protein extracted from soybeans. The powdered form of soy formula is generally preferred for babies with Galactosemia.
What is the primary provider for a newborn?
For some parents, their baby will be in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The primary provider is the neonatologist, who specializes in the care of newborns with serious illnesses.
Can galactose build up in blood?
Galactitol build-up in blood or urine. A blood or urine sample may be taken to determine if there is an excessive amount of galactitol, the toxic substance made when galactose cannot be processed by the body. The presence of galactitol can support a diagnosis of Classic Galactosemia.
Can galactosemia be diagnosed with a low GALT?
Classic Galactosemia will typically be diagnosed if GALT enzyme activity is low. At this point, the doctor may request the test be re-run to confirm diagnosis, or may take another blood sample for genetic testing. Some states may also perform an additional test to measure Total Galactose (galactose + Gal-1p).
Can you have galactose after birth?
These symptoms can occur immediately after birth as a result of consuming too much galactose ( either through breast milk or dairy-containing formula). While waiting for confirmation of a Galactosemia diagnosis, your doctor will suspend dairy products and breastfeeding.
What is galactosemia in toddlers?
Getting used to solids, food labels, and the world of feeding toddlers. Galactosemia may have an influence on certain milestones, particularly as it pertains to the adventure of new varieties and textures of baby and table foods, as well as self-feeding.
When to test for galactitol in infant?
After diagnosis, your doctor will likely continue to test for increased levels of Gal-1p, or for levels of galactitol, throughout the first year of your child's life.
Can galactosemia cause delayed speech?
However, there are some Galactosemia-related signs of delayed development—for example, apraxia or dysarthria (e.g., delayed language, inability to move lips or tongue to say words, slurred or mumbled speech)—that might indicate you should talk to your pediatrician.
What is the most severe form of galactosemia?
Classic galactosemia, the most severe form of the disease, can result in hepatomegaly (an enlarged liver), cirrhosis, renal failure, cataracts, vomiting, seizures, hypoglycemia, lethargy, brain damage and ovarian failure.
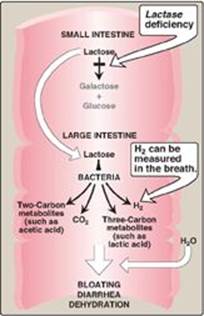
What are the two carbs in milk?
The major carbohydrate in human milk is lactose. When lactose is digested, it breaks down into two molecules: glucose and galactose. Galactosemia is a rare genetic metabolic disorder that affects an individual’s ability to metabolize (process) galactose . Galactosemia is caused by errors in the genes for the three main enzymes responsible ...
What is the condition that affects the body's ability to process carbs in breast milk?
Rebecca’s second child was born with galactosemia, a rare condition that affects the way the body can process the carbohydrate in breast milk. Rebecca recalls the events that led up to the diagnosis and shares more information about the condition.
Is galactosemia inherited?
Galactosemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Inheriting a defective gene from both parents is required to show the disease. Offspring that inherit one normal gene and one defective gene (heterozygotes) are carriers of the disease but do not show symptoms.
Is Savannah a healthy baby?
However, my doctor recognized that the health benefits of breastfeeding outweigh the potential risks of continued milk exposure for these infants. Savannah is now a healthy, smart, strong, and amazing little three-year-old. We have not had to do any further testing, since it was not recommended to us.
Is Duarte galactosemia asymptomatic?
Infants with Duarte galactosemia who consume human milk or a lactose-containing formula are typically, but not always, asymptomatic. Many physicians believe that the Duarte variant of galactosemia does not result in clinical disease either with or without dietary intervention. However, there are reports to the contrary and no adequately powered study either confirming or refuting this assumption has been reported. Be-cause available data about the neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with Duarte variant galactosemia are conflicting, further studies are warranted to determine the long-term outcomes and whether the dietary intake of galactose in the first year of life influences the outcomes. Before such additional studies are performed, a decision con-cerning what to do about galactose in the diet is left to the discretion of the parents and their physician.
How do babies inherit galactosemia?
Classic galactosemia is an autosomal recessive condition. Babies inherit the condition when each parent passes down a nonworking GALT gene to their baby.
What vitamins are good for galactosemia?
Vitamin supplements (calcium, vitamin K, vitamin D) Children who receive early and ongoing treatment for classic galactosemia can have healthy growth and development. Some children with classic galactosemia who receive treatment early still show delays in learning, development, speech/language, and motor skills.
What is the cause of Duarte galactosemia?
Babies with Duarte galactosemia typically show few or no signs or symptoms. Classic galactosemia is caused by a change in the GALT gene. This gene gives your body instructions for making the GALT enzyme. GALT breaks down galactose into glucose and other substances that your body uses for energy.
What is the most common type of galactosemia?
Classic galactosemia (galactosemia type I) Galactokinase deficiency (galactosemia type II) Galactoepimerase deficiency (galactosemia type III) The type your baby has depends on which enzyme is not working properly to break down galactose. Classic galactosemia is the most common type of galactosemia and results when an enzyme called GALT, ...
How long does it take for a baby to show signs of galactosemia?
Careful monitoring and early treatment will help your baby stay as healthy as possible. Signs of classic galactosemia often appear within a few days of birth. Drinking milk the body cannot break down can cause symptoms. Babies with Duarte galactosemia typically show few or no signs or symptoms.
How many chances of having a child with galactosemia?
In most cases, families have no history of the condition until the birth of a child with classic galactosemia. Parents who already have a child with classic galactosemia still have a 1 in 4 chance of having another child with classic galactosemia. This 1 in 4 chance stays the same for all future children.
Can a baby make enough GALT?
Without a working GALT gene, your baby cannot make enough working GALT enzyme. As a result, their body cannot properly break down and get rid of galactose. High levels of galactose and other undigested sugars can damage their body. Classic galactosemia results in very little to no working GALT enzyme.
What to do if your child has galactosemia?
This test will include both a blood and urine sample. If your child has galactosemia, your doctor will work with you to plan a diet. Lactose and galactose are taken out of their diet. Instead, they’re given soy-based formula and must avoid milk or milk byproducts.
How do you know if your baby has galactosemia?
If your newborn has classic galactosemia, they’ll appear normal at birth. Symptoms start to show up within a few days after they begin to drink breast milk or formula with lactose -- the milk sugar that contains galactose. Your baby first loses their appetite and starts vomiting.
What is a newborn screening?
Every baby born at a U.S. hospital is given what’s called a newborn screening. A blood sample is taken from a heel stick (a tiny cut in the baby’s foot) and it is tested for several conditions. Galactosemia is one of them. If your baby shows signs of the illness, your doctor will suggest a follow-up test to confirm.
What vitamins should I take for my baby?
In addition, your child may need to take vitamin and mineral supplements such as calcium, vitamin C, vitamin D, and vitamin K. Some babies have a form of the condition called Duarte galactosemia (DG), which is milder than the classic form (type I).
What happens if a baby has cataracts?
The disease leads to severe weight loss and your baby struggles to grow and thrive. Without treatment, over time your child may develop cataracts and can be susceptible to infections.
What are the three main types of galactosemia?
This causes galactose to build up in the blood, creating problems, especially for newborns. There are three main types of galactosemia: Classic (type I) Galactokinase deficiency (type II) Galactose epimerase deficiency (type III) Type I occurs in about 1 in every 30,000 to 60,000 people. Type II and type III are less common.
When do girls with galactosemia need hormones?
Girls with galactosemia may require hormone treatment when they reach puberty. It’s important that parents of a child with galactosemia work with a health care team to find ways to help them live with the condition and its effects on their daily life. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Pinterest Email Print.
What are the interventions for galactosemia?
Nursing Interventions. Nursing interventions for a child with galactosemia include: Milk substitution. A soy-based formula, meat-based formula, or Nutramigen, or another soy-based formula that contains no galactose should be substituted into the infant’s diet. Dietary restrictions.
What is the assessment of a child with galactosemia?
Nursing Assessment. Assessment of a child with galactosemia include: Physical examination. Assess the child’s presenting symptoms, especially after ingestion of galactose. Nutritional intake. Assess the child’s dietary needs, and the family caregivers understanding of the disorder to establish a strict diet regime.
What enzymes are associated with hypergalactosemia?
Galactokinase converts galactose to galactose-1-phosphate and is not a common deficiency. Uridine diphosphate (UDP) galactose-4-epimera se epimerizes UDP galactose to UDP glucose and is also uncommon. GALT is responsible for hereditary galactosemia and is ...
What enzyme is responsible for galactosemia?
GALT is responsible for hereditary galactosemia and is the most common deficiency. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of galactose-1-phosphate and UDP glucose to UDP galactose and glucose-1-phosphate. Individuals with GALT deficiency manifest abnormal galactose tolerance.
What is galactosemia in 2021?
Updated on February 11, 2021. 0. ADVERTISEMENTS. Galactosemia is a recessive hereditary metabolic disorder in which the enzyme necessary to convert galactose into glucose is missing.
What is the most common enzyme deficiency that causes hypergalactosemia?
First described in a variant patient in 1935 by Mason and Turner, galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT) deficiency is the most common enzyme deficiency that causes hypergalactosemia.
What is galactose free milk?
The caregivers identified the appropriate food for the infant. The caregivers provided galactose-free milk as a substitution for breastmilk. The caregivers understood the disease process and the care of the newborn with galactosemia.

Sources of Diet Guidelines
- Unfortunately, clinics do not provide uniform direction to their parents and patients, the recommended diet for Classic Galactosemia is somewhat controversial. Below is a list of diet resources that some parents follow, however, please always check with your own clinic for diet …
Galactosemia vs Lactose Intolerance
- In Galactosemia, the body does not produce a functional Galactose-1-Phosphate-Uridylyltransferase enzyme thus the body is not able to fully metabolize galactose sugars. One method galactose is introduced to the body is through metabolization of lactose, a "complex" sugar that contains a galactose sugar and a glucose sugar. Excessive galactose in the body lea…
Unacceptable Ingredients
- Since actual products change on a regular basis it is imperative that you re-read every label every time you buy. Various parents and dietitians have put together this list of unacceptable ingredients in an attempt to simplify the ingredient dilemma. Please, remember to always check with your clinic and dietitian. Gather all information available and then make your own decision. …