
What is the best diet for dog with bladder stones?
- Natural ingredients. Every dog deserves a high-quality diet made from natural ingredients. ...
- High moisture content. Diluting the urine is one of the best ways to dissolve existing stones and prevent future stones from forming. ...
- Moderate protein levels. ...
- Complete and balanced. ...
Should dogs really be eating raw food?
Ten Reasons to Start a Raw Dog Food Diet
- Your Dog is a Wolf. Well, kind of. ...
- Raw Food Tastes Better. There’s a time and a place for fast food in everybody’s life, but it’s hardly something that you’ll want to live off for every meal ...
- Raw Food Means One Ingredient. ...
- Kibble Damages the Doggy Digestive System – Raw Food Enhances it. ...
- Raw Food Freshens Breath and Cultivates Healthy Teeth. ...
Can dog with IBS be fed a raw diet?
We do not claim that a raw diet “cures” Canine IBD - but feeding dogs a high quality (human grade, unadulterated), fresh meat-and-organ based diet their digestive systems are designed to metabolize enables those systems to return to physiological balance.
What are the best foods to eat without a gallbladder?
– Caffeine-free tonics – All lean, tender meats – Skinless poultry – Fish, shellfish – Eggs – Soy beans (including tufu) – Low-fat and skim milk and products – Whole grain crackers, graham crackers – White or brown rice – Noodles/spaghetti – All vegetables except tomatoes
What foods heal the gallbladder?
Healthy Foods for the GallbladderFresh fruits and vegetables.Whole grains (whole-wheat bread, brown rice, oats, bran cereal)Lean meat, poultry, and fish.Low-fat dairy products.
How can I help my dogs gallbladder?
Appetite stimulants, gallbladder support supplements, antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, pain medications, anti-nausea medications, and surgical removal of the gallbladder are all options for treating gallbladder disease.
What should I feed my dog with gallbladder sludge?
A low-fat, high-protein diet has been advanced for the management of canine gallbladder mucocele (11) . Such a diet, for instance a dry, complete food with ≤ 10 % crude fat and ≥ 40% crude protein, might also benefit non-surgical control of canine cholelithiasis. ...
How do you get rid of sludge in a dog's gallbladder?
Biliary sludge occurs more commonly in older dogs. Its pathophysiology is poorly understood, and it is often treated with internal medicine, with a low-fat diet and medications, such as ursodeoxycholic acid, S-adenosylmethionine and other drugs [1, 3, 4, 8, 11, 17, 25].
How long can a dog live with gallbladder problems?
Results: Of dogs surviving at least 14 days after diagnosis, median survival times were 1802 (95% confidence interval [CI], 855-not reached) days, 1340 (95% CI, 444-1340) days, and 203 (95% CI, 18-525) days, for the surgical, medical, and medical then surgical treatment groups, respectively, and differed significantly ...
How long does it take for gallbladder sludge to go away in dogs?
Conclusions and Clinical Importance. Biliary sludge was prevalent, affected dogs remained asymptomatic, and it rarely resolves in healthy dogs over a period of 1 year.
What can I feed my dog with liver and gallbladder problems?
Good proteins to feed for liver disease are eggs for the most bioavailable protein and choline content, poultry and a little fish such as sardines, salmon and cod. Proteins to reduce or avoid would be red meats high in phosphorus.
Can a dog recover from gallbladder problems?
The condition may be inherited in some breeds, including Shetland Sheepdogs. Underlying diseases can also predispose dogs to the condition. Some mildly affected dogs can improve with medications alone; however, most will require surgery to remove the gallbladder.
What causes sludge in gallbladder dogs?
Gallbladder mucocele formation in dogs is an emerging and deadly disease. Current knowledge suggests that genetic and metabolic factors are involved in altering the gallbladder lining function and facilitating the underlying or concurrent hormonal abnormalities.
Does gallbladder sludge cause pain in dogs?
In some cases, the wall of the gallbladder is damaged, and bile leaks into the abdomen causing severe abdominal infection and inflammation, which can be fatal. Loss of appetite, abdominal pain, jaundice, fever, and vomiting are common signs. The dog may be in a state of shock due to abdominal inflammation.
How serious is gallbladder sludge in dogs?
When the gallbladder becomes distended with sludge, its blood supply can become impaired making it prone to rupture. Once ruptured, bile can leak into the abdomen causing bile peritonitis which can be life-threatening.
Should I have my dogs gallbladder removed?
Dogs can live without a gallbladder but may require special care to support the digestive process. You will need to watch for complications, give your pet all required medications, check the incision, and feed them food that's easy to digest.
What is gallbladder disease in dogs?
Similar in appearance to the urinary bladder, the gallbladder is a small organ that holds fluid within the body of humans and some animals.
What tests can be done to check gallbladder in dogs?
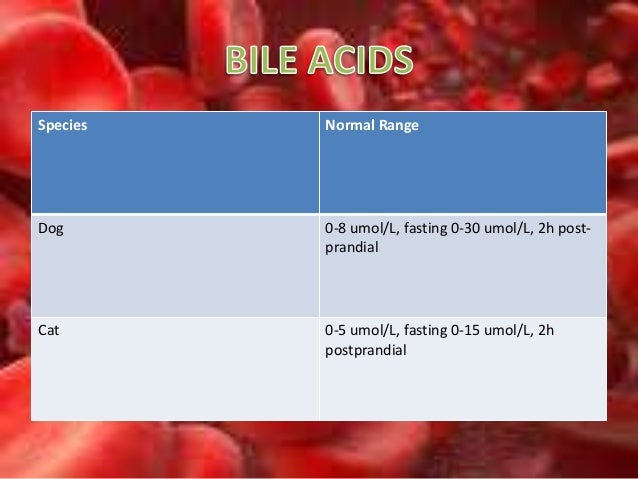
There are a variety of tests that your veterinarian can perform to diagnose gallbladder disease in your dog. X-rays and ultrasounds may show gallstones, mucoceles, cysts, or tumors inside of the gallbladder. Blood tests may show elevated liver enzymes, bile acids, cholesterol, and bilirubin.
What is the term for a gallbladder that is swollen and has mucus?
This inflammation of the gallbladder is called cholecystitis. Gallbladder mucoceles: In addition to inflammation, a stuck gallstone can cause mucus to build up in the gallbladder and create a mucocele. A mucocele is simply an accumulation of mucus in the gallbladder that causes the gallbladder to stretch and be larger than normal.
Why does the gallbladder rupture?
1 This usually occurs due to severe inflammation or trauma. Gallstones: These stones are formed from cholesterol, bilirubin, and other components in very saturated bile.
What causes bile to back up?
Tumors usually obstruct the flow of bile which causes it to back-up and therefore secondary problems result. Cysts: Cysts are growths that can obstruct the flow of bile into and out of the gallbladder. These cysts are usually filled with mucus.
What is the treatment for gallbladder disease?
Treatment will address both the symptoms as well as the underlying problem, so a variety of medications, supplements, and sometimes even surgery may be recommended .
Why does my dog's vomit turn yellow?
Stomach ulceration due to gallbladder disease may produce blood in the vomit or stool. The blood is usually bright red in the vomit but a dark black in the stool. Jaundice is the most recognizable and distinct sign of liver or gallbladder disease in a dog. Jaundice causes the skin, mucous membranes, and the whites of the eyes to turn yellow due ...
What is the treatment for gallbladder infection?
Treatment usually consists of removal of the gallbladder and appropriate antibiotic medication to treat infection. The outlook is good if surgery and appropriate antibiotics are started early but is less favorable if diagnosis and treatment are delayed.
Where is bile stored in dogs?
Bile is stored in the gallbladder and is released into the small intestine through the bile duct. There are a few common diseases that a dog can experience relating to the gallbladder or bile duct. 1. Obstruction of the Bile Duct.
What causes a rupture of the gallbladder?
Rupture of the gallbladder or bile duct is most often due to gallstone obstruction, inflammation of the gallbladder, or blunt trauma. Rupture of the bile duct may also occur as a result of cancer or certain parasites.
What happens if a gallbladder ruptures?
Rupture leads to leakage of bile into the abdomen, causing a serious condition called bile peritonitis, which may be fatal if the rupture is not repaired. Treatment includes surgery, which consists of placing a stent in the bile duct, removing the gallbladder, or connecting the gallbladder with the small intestine.
What causes a gallbladder to be compressed?
Tissue swelling, inflammation, or fibrosis can cause compression of the bile duct. Diagnosis is based on laboratory tests, x-rays, and ultrasound. If gallstones are the cause of obstruction, the gallbladder may need to be removed.
Why does my dog have cholecystitis?
Loss of appetite, abdominal pain, jaundice, fever, and vomiting are common signs. The dog may be in a state of shock due to abdominal inflammation.
What organs help with digestion?
Diseases of the Gallbladder and Bile Duct: First a quick orientation as to how this organ contributes to the body. The liver secretes bile, a substance that assists with digestion and absorption of fats and with elimination of certain waste products from the body.
What is the purpose of the gallbladder in dogs?
Its purpose is to collect and transport bile secreted by the liver. When bile reaches the small intestine, its job is to digest some vitamins and fats. Bile also helps to get rid of waste matter in the dog’s body.
What are the symptoms of gallbladder problems in dogs?
In most cases, pet parents learn about problems with the gallbladder in dogs when the animal shows signs of distress, such as abdominal pain, vomiting, or loss of appetite. Canine gallbladder problems can become very dangerous very fast if they aren’t treated right away.
How to tell if a dog has gallbladder problems?
Common symptoms of gallbladder problems in dogs include: Abdominal pain. Loss of appetite. Vomiting. Diarrhea. Jaundice (yellow color to the eyes, skin, and mucus membranes like the gums) Fever. Stomach ulceration with bright red blood in vomit and dark black blood in stool. Lab work shows irregular liver values.
Why does my dog have a gallbladder?
In addition to mucoceles, the gallbladder of a dog can become obstructed by: Cancer in a variety of areas, including but not limited to, the pancreas and liver. A high-fat diet that may result in supersaturated levels of cholesterol in the bile. Excessive amounts of fat in the blood caused by pancreatitis.
How long do you have to keep a dog on antibiotics after a syringe?
Time is crucial when it comes to life or death. Antibiotics are most often necessary for four to six weeks postoperatively. Stay current with your dog’s bloodwork, and as your dog ages, have bloodwork screened at least twice a year. Keep your dog at a healthy weight, and do not allow him or her to become overweight.
What to do if my dog is showing distress?
Time is of the essence, so if your dog is showing signs of distress of any of these symptoms, seek urgent veterinary care immediately.
Can a dog have a mucocele?
If the gallbladder gets too much bile and mucus and gets swollen or distended, a gallbladder mucocele can happen. The bile gets backed up, it can’t flow properly and do its job. The dog gets weak and tired, might vomit, have a fever, and exhibit signs of pain.
The Liver
The liver is an accessory organ in the GI tract that performs numerous functions. It plays an important role in filtering out toxins to prevent them from being absorbed by the body. It also metabolizes different substances and chemicals to help in the absorption of certain medications and supplements.
The Gallbladder
Between different lobes of the liver lies the dog’s gallbladder, a sac-like organ that serves as a storage for the bile that the liver produces. The gallbladder is connected to the bile duct which empties into the intestine.
Common Types of Gallbladder Disease in Dogs
Diseases that affect the dog’s gallbladder often result in a wide variety of symptoms, depending on the specific cause. Dogs suffering from any form of gallbladder disease will often present with some degree of abdominal discomfort, a decrease in appetite, and generalized weakness.
Is Surgery Needed for Gallbladder Disease in Dogs?
Several conditions can affect a dog’s gallbladder, but not all require surgery. If your dog has gallstones, for example, they could potentially be treated through medication and diet. Those gallstones could be noticed incidentally when running diagnostics like x-rays for another problem.
Gallbladder Removal for a Mucocele in Dogs
A gallbladder mucocele is one condition that can be life-threatening, and it almost always requires surgical removal of the gallbladder. This occurs when the bile stored in a dog’s gallbladder thickens to become mucus-like and cannot flow to the intestine. The mucus creates a blockage in the gallbladder, which can lead to rupture and death.
Procedure for Gallbladder Removal in Dogs
Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy) is a serious surgical procedure with the potential for complications. Surgery involves going into the abdomen to remove your dog’s gallbladder.
Aftercare for Dog Gallbladder Removal
Dogs can live without a gallbladder but may require special care to support the digestive process. You will need to watch for complications, give your pet all required medications, check the incision, and feed them food that’s easy to digest.
Importance of Liver Function
The liver is a vital powerhouse of the internal organs. It filters, processes, and manages essentially everything within the body, whether it is your dog’s or your own. The liver has two lobes; it is located over the gallbladder and portions of the intestines and pancreas. Altogether, these organs work to digest, process, and absorb nutrients.
Causes of Canine Liver Disease
Poor diet may be a cause of liver disease. It can trigger the right genetic conditions for liver disease. While diet is generally not the sole culprit, it is often a minor player in the factors adding up to liver disease. Stress is definitely part of the pathogenesis of this condition.
Symptoms of Dogs with Liver Disease
If your dog has liver disease, there are a number of potential signs and symptoms. They may be subtle at first, so look for them in combinations and to show themselves consistently.
Diagnosing Chronic Liver Failure
The vast majority of the symptoms of liver disease are not necessarily specific to that condition, which makes a diagnosis from a veterinarian important. A vet visit as soon as symptoms arise is the best option. The veterinarian will run a gamut of tests. Blood tests for elevated liver enzymes often do the trick.
Dietary Guidelines
Never make abrupt changes to your dog’s dietary arrangements. Instead, make gradual alterations, receiving advice from your veterinarian if you have uncertainties. Feed your dogs with the liver disease several smaller meals a day. The liver can more easily process these smaller amounts.
Which Foods Should You Include?
Safe dairy products are great for your dog’s diet. Select ricotta cheese, yogurt that does not contain Xylitol, and cottage cheese. They aid digestion while producing less ammonia than meats will. Select dairy products that have low quantities of fat and salt. Also, remember that cow cheese is more difficult to digest than goat cheese.
Which Foods Should You Avoid?
Foods that contain high levels of copper should be avoided because copper buildup can lead to worsening liver conditions. You will find that most organ meats contain high levels of copper, particularly the livers of cows. The livers of turkeys and chickens are low in copper and thus are more acceptable for your dog’s diet.
